ChatGPT Atlas Rattles Google as Stock Drops
The Day The Ground Shifted

On Tuesday, October 21, 2025, the technology world witnessed a power shift. As OpenAI unveiled ChatGPT Atlas, its artificial intelligence-powered web browser, the stock market delivered an immediate verdict: shares of Alphabet, Google’s parent company, dropped sharply, closing down 2.4% amid investor fears that the very foundation of internet search is changing .
This wasn’t just another product launch. For the first time, the company behind ChatGPT stepped directly onto Google’s home turf with a browser that reimagines how people interact with the web. The market’s reaction—Alphabet’s stock fell as much as 3.4% during trading—reflects deep-seated concerns about Google’s future in an AI-dominated landscape .
A Billion-Dollar Tumble
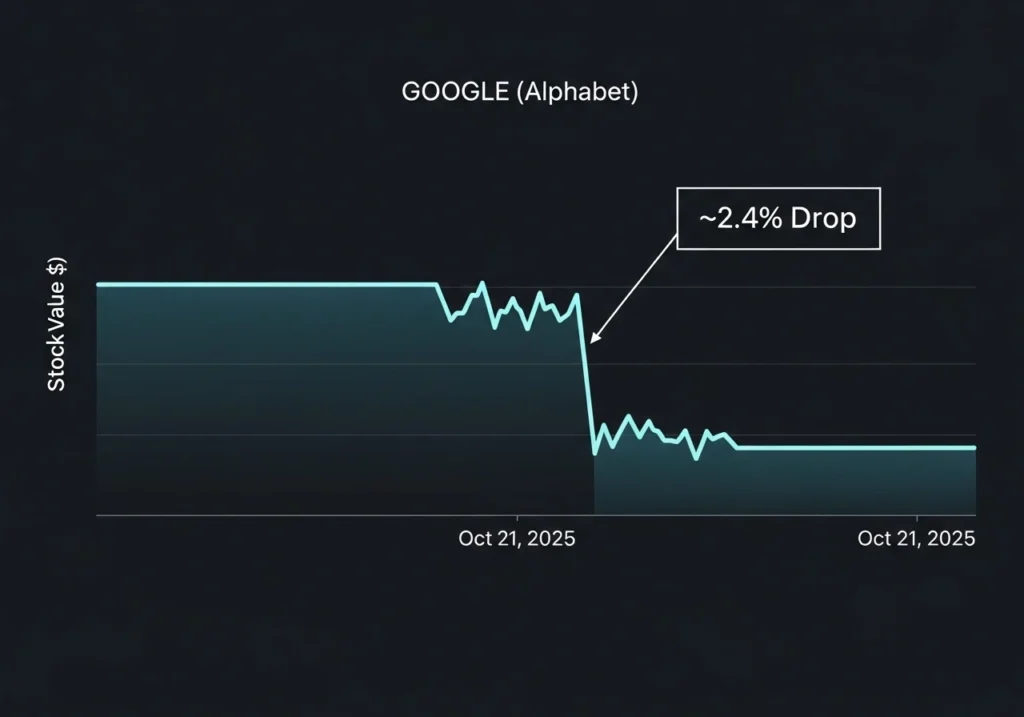
The numbers tell a stark story of market anxiety. Alphabet’s shares closed at $250.46, down from the previous close of $256.55, wiping billions from the company’s market capitalization . This decline occurred despite what should have been a strong day, with the broader market showing positive momentum .
Why such a dramatic response? The answer lies in Google’s core business model. Search advertising generates over half of Alphabet’s revenue, creating legitimate investor concern about how AI-powered browsers and search engines could impact the company’s largest revenue stream . The conversational, answer-providing nature of tools like ChatGPT represents a fundamental challenge to Google’s traditional link-based results .
“Investors have been increasingly concerned about the launch of AI-powered browsers and search engines when it comes to Alphabet, which has long dominated the search business,” noted Bram Berkowitz of The Motley Fool .
More Than a Browser: The ChatGPT Atlas Revolution
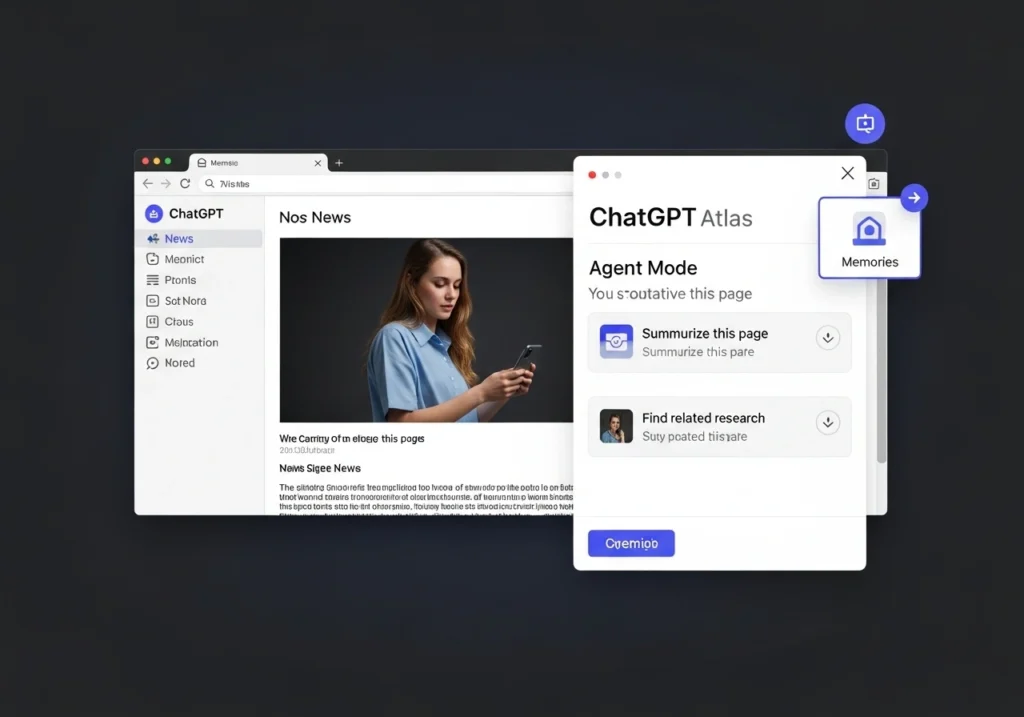
OpenAI isn’t merely launching another browser; it’s proposing a new paradigm for web interaction. ChatGPT Atlas represents what CEO Sam Altman called “a rare, once-in-a-decade opportunity to rethink what a browser can be” . Rather than just displaying webpages, Atlas integrates ChatGPT directly into the browsing experience, creating what the company describes as “a true super-assistant that understands your world and helps you achieve your goals” .
Several groundbreaking features set ChatGPT Atlas apart:
- Browser Memories: Atlas can optionally remember context from sites you visit and use this information to personalize future assistance. Imagine asking “Find all the job postings I was looking at last week and create a summary of industry trends”—and having ChatGPT deliver exactly that .
- Agent Mode: This premium feature allows ChatGPT to take actions on your behalf, such as researching, booking appointments, or online shopping. As Altman explained, “It’s using the internet for you” . This capability is available in preview for Plus, Pro, and Business users .
- Built-in Privacy Controls: Understanding the sensitivity of such deep integration, OpenAI has included extensive privacy controls. Browser memories are optional, and users can view, archive, or delete them. The company also states that by default, it doesn’t use browsing content to train its models .
For college student Yogya Kalra, an early tester of ChatGPT Atlas, the impact was tangible. “I used to switch between my slides and ChatGPT, taking screenshots just to ask a question,” Kalra said. “Now ChatGPT instantly understands what I’m looking at, helping me improve my knowledge checks as I go” .
An Uphill Battle Against a Giant

Despite the impressive technology, ChatGPT Atlas faces a daunting challenge. Google’s Chrome browser has amassed approximately 3 billion worldwide users and has been steadily adding AI features from Google’s Gemini technology .
The situation echoes history. When Google released Chrome in 2008, Microsoft’s Internet Explorer was so dominant that few believed a new browser could mount a formidable threat. Yet Chrome’s faster performance and better features ultimately upended the market . Now, OpenAI hopes to repeat that disruptive playbook against Google itself.
Analyst Paddy Harrington of market research group Forrester acknowledges the challenge of “competing with a giant who has ridiculous market share” but also recognizes the shifting landscape .
The timing of this launch is particularly noteworthy. It comes just months after a federal judge rejected a Justice Department request to force Google to sell its Chrome browser in an antitrust case, partly because he believed AI advancements were already reshaping competition .
Google’s Defense: AI and Beyond
Google isn’t standing still. The company has aggressively integrated its Gemini AI model into Chrome, allowing U.S. desktop users to access AI assistance without switching windows . Google has also deployed AI Overviews in search results, providing conversational summaries similar to ChatGPT’s output .
Most analysts have been impressed with user engagement regarding Google’s AI-powered overviews . The company’s extensive resources and technical expertise position it to compete effectively in the AI space.
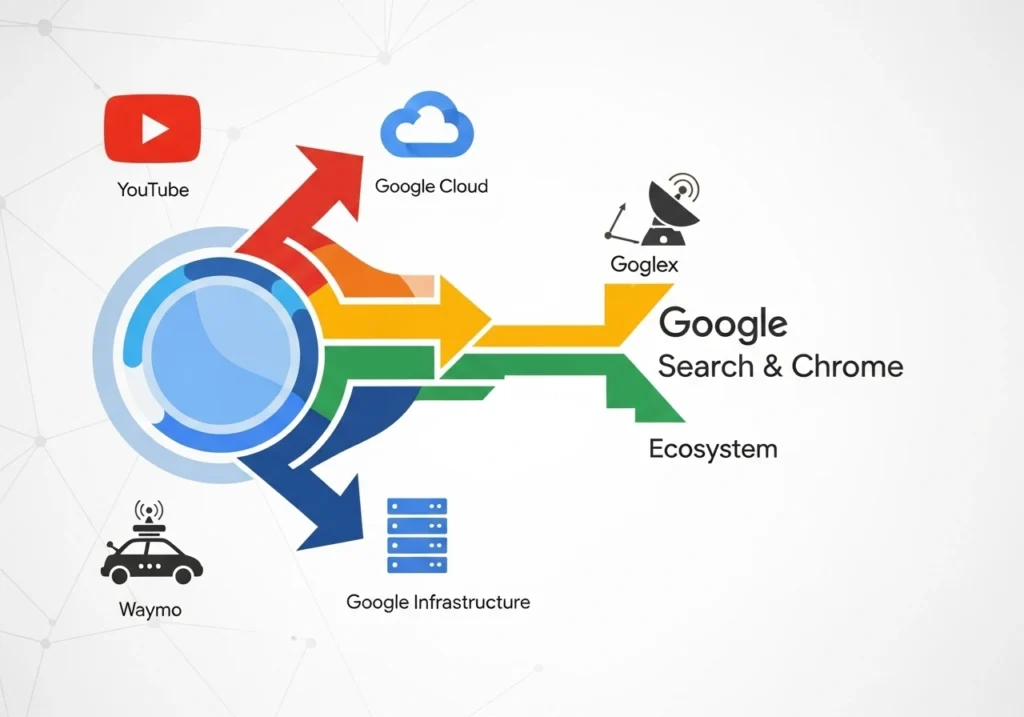
Beyond search, Alphabet’s diverse business portfolio provides additional resilience. The company owns spectacular businesses with strong growth prospects, including YouTube, Google Cloud, Waymo, and various technology initiatives . Google Cloud alone has reached a $50 billion annual revenue run rate and continues to show strong growth .
The Wider Impact: Publishers and the Web’s Future
The rise of AI browsers raises significant questions beyond stock prices. If ChatGPT effectively summarizes information from websites, will users stop clicking on traditional web links? This scenario could further cut off the lifeblood of online publishers who rely on traffic for advertising revenue .
This tension isn’t theoretical. The New York Times and other outlets have already sued OpenAI for copyright infringement, while others, including The Associated Press, have signed licensing deals . How this balance between AI convenience and content creator compensation will be struck remains one of the most critical questions in the digital ecosystem.
The technology itself also faces quality challenges. A recent study of four top AI assistants, including ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini, showed nearly half their responses were flawed and fell short of the standards of high-quality journalism .
What Comes Next in the AI Browser Wars
ChatGPT Atlas launches first on macOS, with versions for Windows, iOS, and Android “coming soon” . But this is just the opening move in what promises to be an extended competitive battle.
All eyes now turn to Alphabet’s third-quarter earnings report, due on October 29, where investors will scrutinize the company’s advertising revenue trends and AI progress . Wall Street expects revenues of $99.75 billion and will pay close attention to management’s strategic outlook for the remainder of 2025 and 2026 .
There’s also speculation that OpenAI might eventually introduce advertising to ChatGPT, a move that would further pressure Google’s core business model . With ChatGPT already boasting over 800 million users, the platform represents a substantial potential advertising network .
A Transformative Moment

The launch of ChatGPT Atlas represents more than a product release—it signals a fundamental shift in how we interact with the digital world. The traditional model of typing queries into a search bar and scanning through blue links is now facing its most serious challenge.
As one analyst put it, the conversational experience in a browser may become “a great equivalent” for how people use the internet in the future . For Google, this means adapting its legendary search business to an AI-first world. For users, it promises more assistance and less friction in finding information and completing tasks online.
The stock market’s reaction to ChatGPT Atlas reveals both the scale of the opportunity and the significance of the threat. In the battle for the future of the web, the opening shots have been fired.